Publications
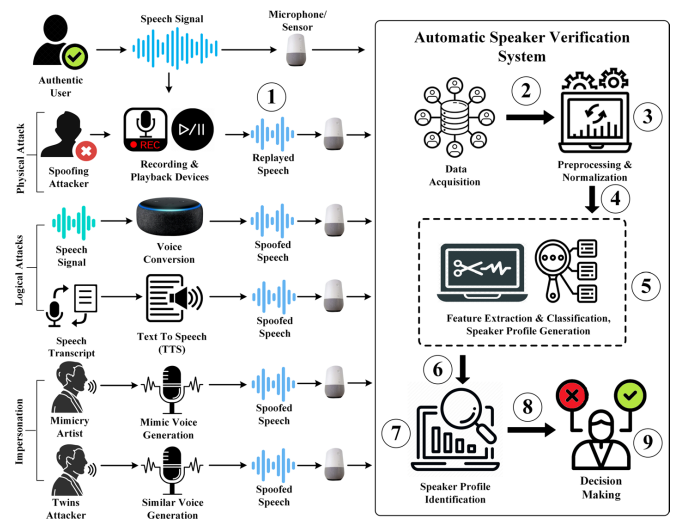
Unmasking the Audio Illusion: A Survey on Spoofing and Deepfake Detection
Aarthi S, and Akshay Agarwal
IEEE International Joint Conference on Biometrics
Abstract: This paper explores the growing practice of manipulating audio to create fakes using deep learning algorithms. It examines methods like speech synthesis, audio splicing, and voice cloning, and various detection algorithms. The paper also discusses the potential impacts of deepfake audio on reputation, fraud, and misinformation, and compares AI and human detection methods.
Robustness Benchmarking of Convolutional and Transformer Architectures for Image Classification
Vishesh Kumar, Shivam Shukla, and Akshay Agarwal
IEEE Transactions on Big Data
Abstract: A study analyzing deep convolutional neural networks (CNNs) across various classification spectrums, including pure CNNs and state-of-the-art Vision Transformers (ViTs), found that different DNNs have varying levels of robustness against image corruption. ViTs, trained on CIFAR10, are highly robust in handling noise corruptions but vulnerable to environmental corruptions. Pure CNNs, while lower in performance, can handle environmental factors better than noise corruption. The study aims to reveal the vulnerabilities of deep learning models and ensure the deployment of correct networks for real-world image classification.

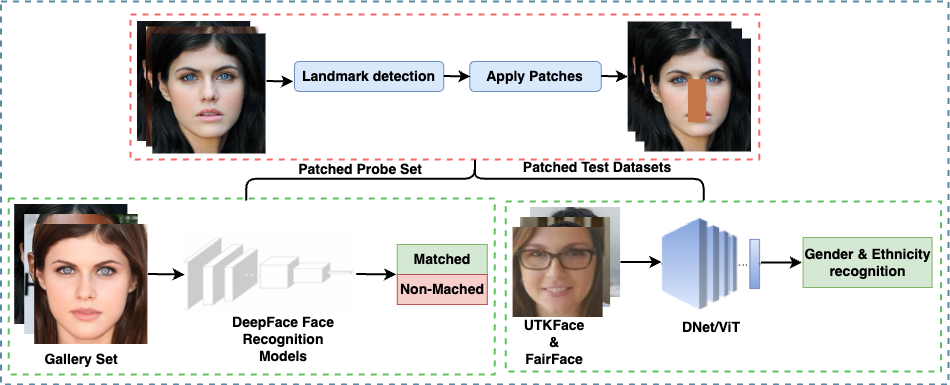
Your Face, Your Privacy: Combating Unauthorized Usage
Atul Kumar, Akshay Agarwal, and Nalini Ratha
IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face and Gesture Recognition (FG)
Abstract: Deep face recognition systems' high performance raises privacy concerns. Users are exploring ways to protect themselves, such as obscuring faces with hands. However, no evaluation exists to show this can bypass face recognition algorithms. A study developed nose and mouth occlusion datasets using synthetic patches and real-life objects. Results showed that patches can fool face recognition networks and soft biometric classifiers, deceiving gender and ethnicity detection.
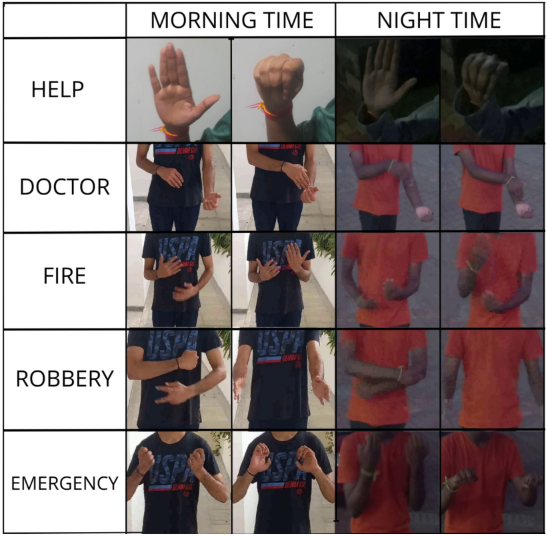
Gesture Recognition for Emergencies: Dataset and Cross-Condition Analysis
Jiya Sinha, Poulomi Bhattacharya, Akshay Agarwal
IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face and Gesture Recognition (FG)
Abstract: Gestures are crucial for nonverbal communication, especially in areas like home automation and medical applications. Research in computer vision, robotics, and HCI has focused on gesture recognition. However, existing studies have limited exploration of Indian ethnicity and gesture capture in nighttime settings. A large-scale hand gesture recognition dataset has been curated, and a benchmark study using state-of-the-art hand detection and gesture classification networks was conducted.
Family Resemblance or Fraud? Face Morphing Attacks on Kinship Verification
Gargi S Yeole, Aarthi S, Shalvika Srivastav, Akshay Agarwal
Second Workshop on Interdisciplinary Applications of Biometrics and Identity Science in IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face and Gesture Recognition
Abstract: This study explores the vulnerability of deep learning models for kinship verification using facial images, particularly when morphing ratios are used. The researchers used a morphed dataset to test their models on original and morphed child images. The results showed a continuous increase in misclassification rates with the increasing percentage of parental features, highlighting the need for more effective verification methods to counter facial morphing risks in real-world applications.
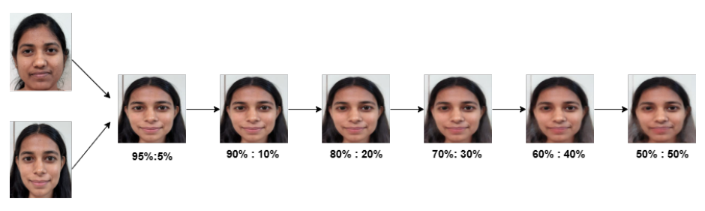
Advancing Facial Age Progression for Occluded Faces
Ankit Birla, Akshay Agarwal
CVPR Workshop and Competition on Affective & Behavior Analysis in-the-wild
Abstract: Face recognition is vulnerable when the age gap between gallery and probe images is high. Accurate age progression is crucial to mitigate this gap and improve face recognition performance. This paper presents a novel approach to facial age progression, addressing occluded faces. Objects occluding the face's key points are detected and inpainted using transformer architecture. This improves facial age progression's robustness and visual quality, making it applicable in security systems and forensic analysis.
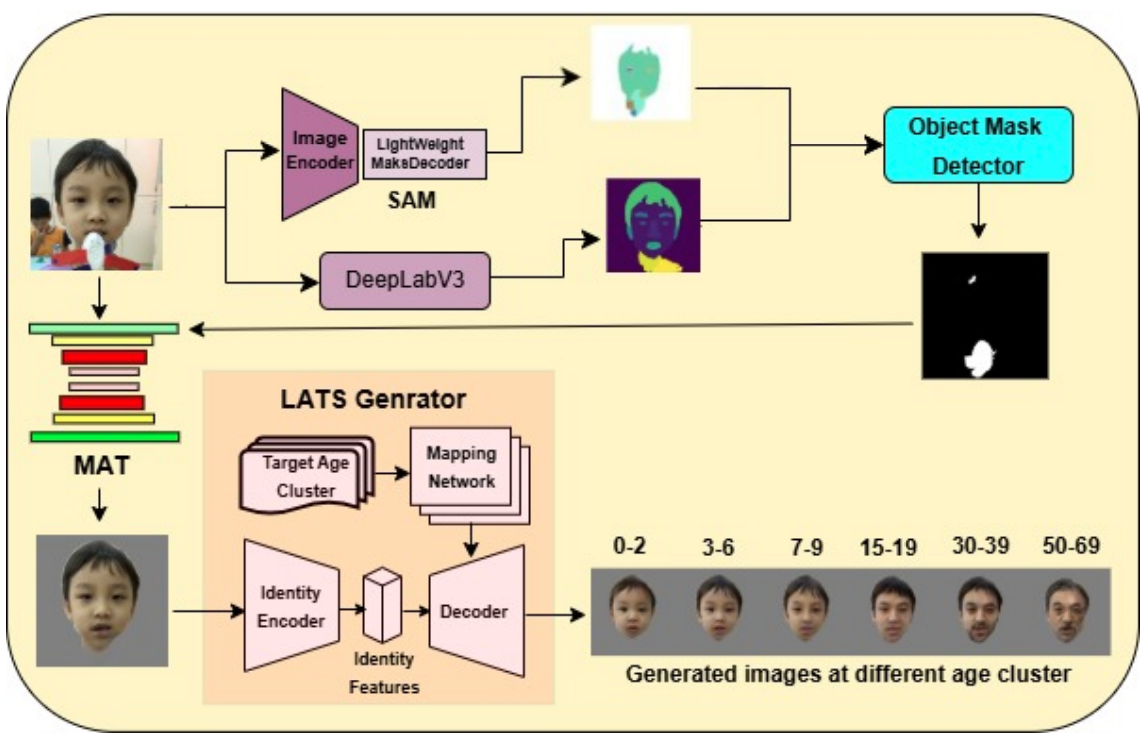
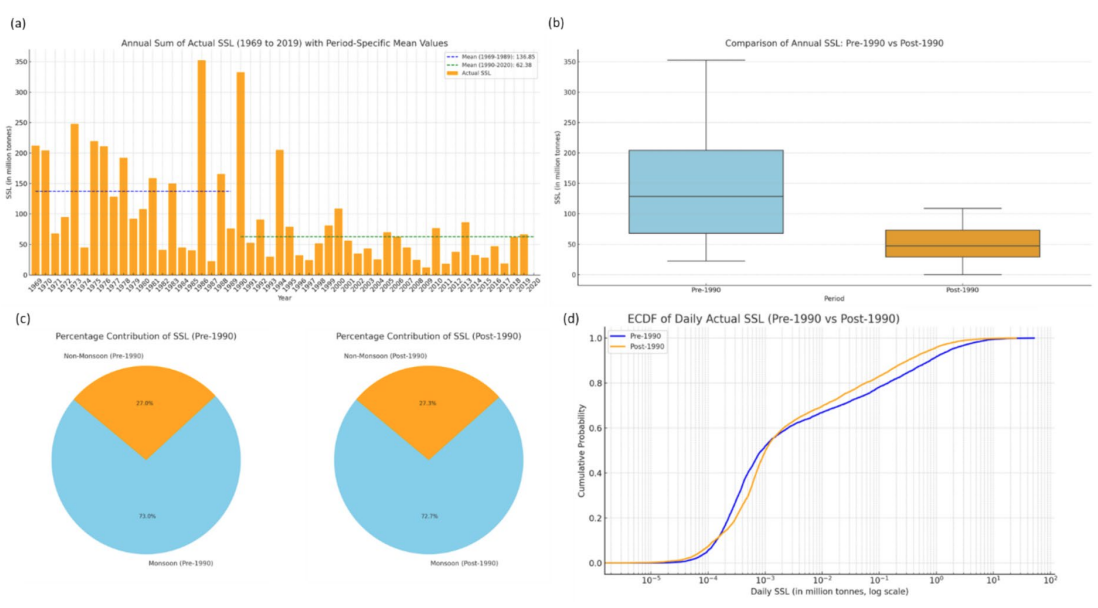
Bayesian‑optimized recursive machine learning for predicting human‑induced changes in suspended sediment transport
Soumya Kundu, Somil Swarnkar, Akshay Agarwal
Environmental Monitoring and Assessment
Abstract: This study examines historical changes in suspended sediment load (SSL) in the Godavari River Basin, revealing a decline post-1990 due to human activities. Tree-based machine learning models improved SSL prediction accuracy, providing insights for sustainable sediment transport modeling under changing hydrological conditions.
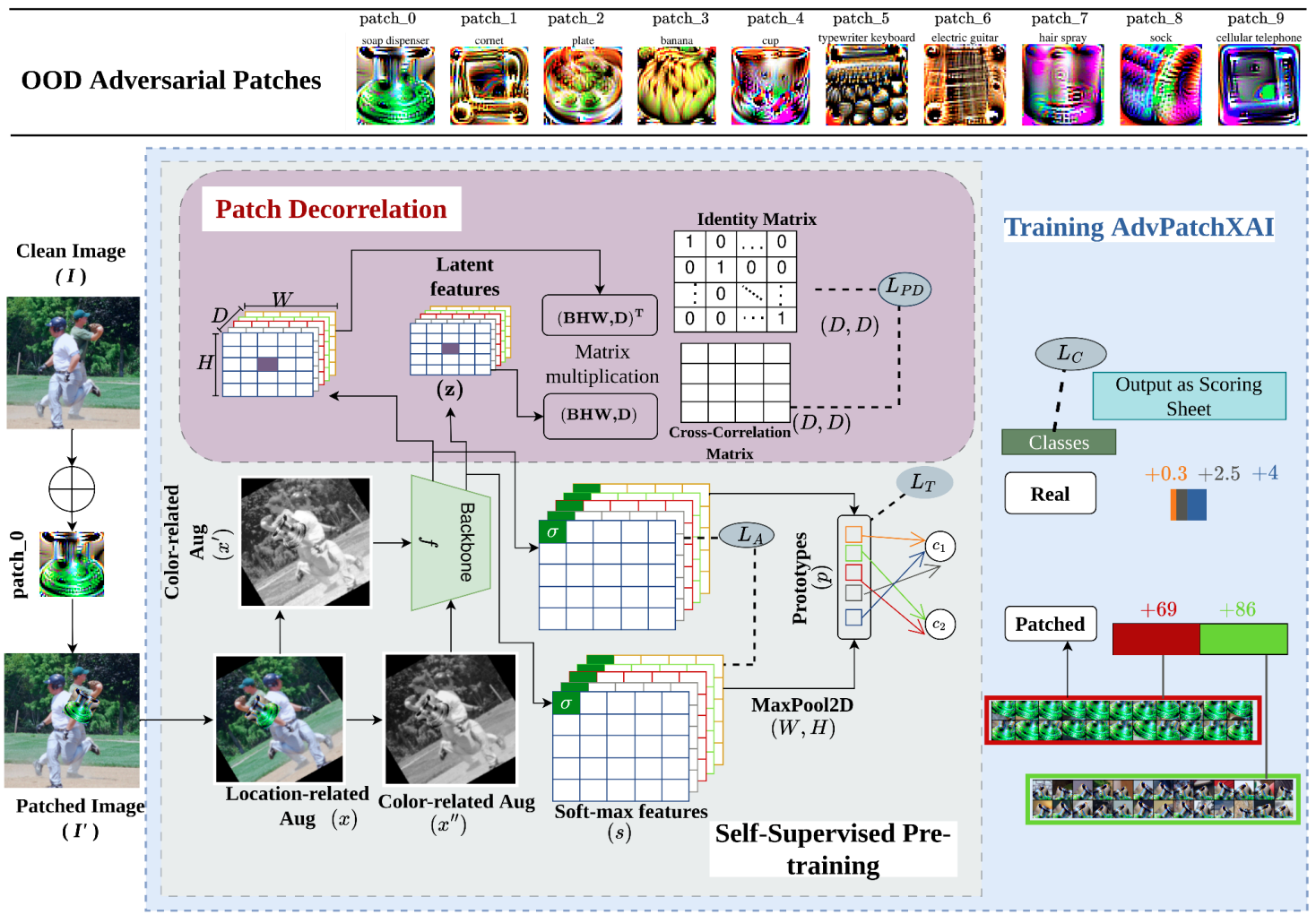
A Unified, Resilient, and Explainable Adversarial Patch Detector
Vishesh Kumar, Akshay Agarwal
IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR)
Abstract: The AdvPatchXAI is a defense algorithm designed to protect Deep Neural Networks (DNNs) from physical adversarial attacks. It uses a novel patch decorrelation loss, self-supervised learning, and a sparse linear layer for classification. The model improves interpretability and correlation with human vision, closing the semantic gap between latent and pixel space and effectively handling unseen patches, thereby enhancing DNN robustness in practical settings.
Detection of identity swapping attacks in low-resolution image settings
Akshay Agarwal, Nalini Ratha
Journal of Information Security and Applications
Abstract: This research proposes a low-resolution identity swap attack detection algorithm to address the challenge of detecting fake face images in low-resolution videos. The algorithm uses artifacts amplification and classification to handle the lack of information content. Extensive evaluations using multiple databases, resolution settings, and attack types demonstrate the strength and effectiveness of the proposed algorithm in in-the-wild settings. The results show superiority compared to existing state-of-the-art works.

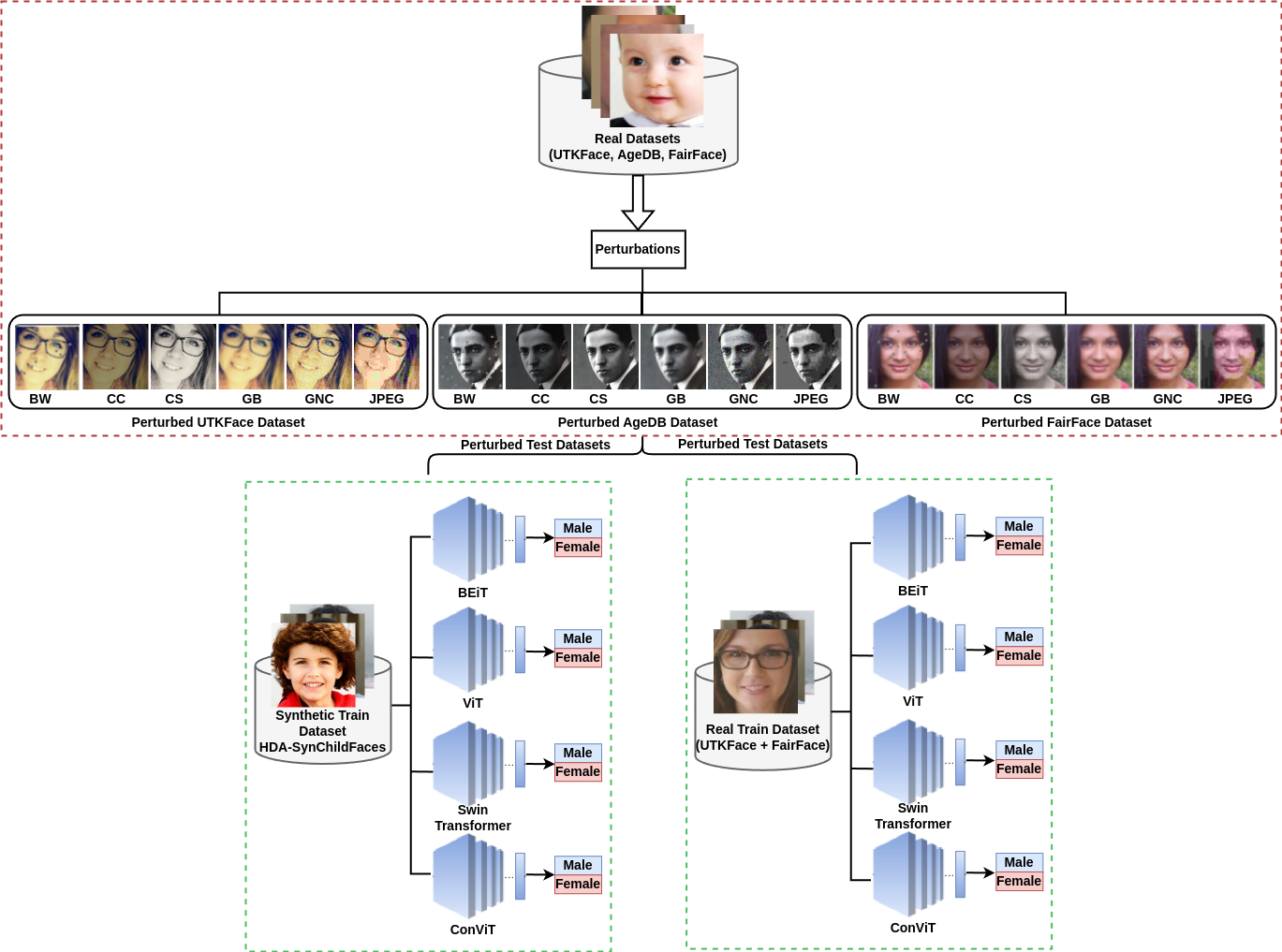
On Which Data Distribution (Synthetic or Real) We Should Rely for Soft Biometric Classification
Manju RA, Atul Kumar, Akshay Agarwal
Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV)
Abstract: Gender identification is vital for human-computer interaction and identity search. While "real" facial images are standard in gender classification, synthetic images are gaining attention due to privacy concerns and advancements in generative networks. However, their effectiveness remains unclear. This study evaluates the performance of gender classification networks trained on real vs. synthetic face images. Using 8 DNNs, including CNNs and ViTs, across 4 datasets and 6 image corruptions, we also employ Grad-CAM and t-SNE for interpretability.
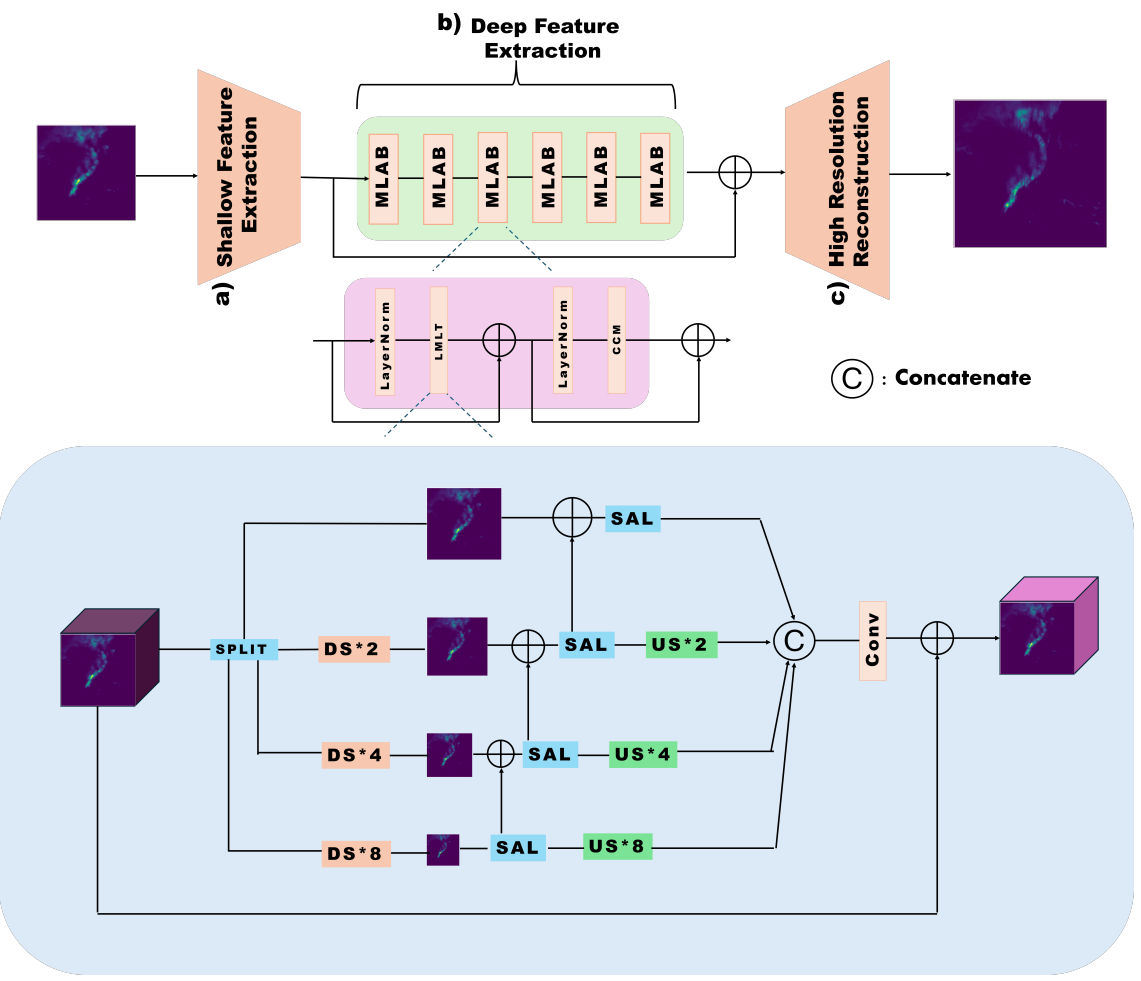
PrecipFormer: Efficient Transformer for Precipitation Downscaling
R. Kumar, T. Sharma, V. Vaghela, S. Jha, A. Agarwal
Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV) Workshops
Abstract: Precipitation downscaling is a crucial challenge in climate modeling and hydrological applications. This paper introduces PrecipFormer, a computationally efficient transformer architecture designed for this task. It builds upon the Low-to-High Multi-Level Vision Transformer mechanism, enabling parallel processing of features at multiple spatial scales and reducing computational overhead. PrecipFormer achieves superior performance compared to state-of-the-art baselines.